Authors:
(1) Jongmin Lee, Department of Mathematical Science, Seoul National University;
(2) Ernest K. Ryu, Department of Mathematical Science, Seoul National University and Interdisciplinary Program in Artificial Intelligence, Seoul National University.
1.1 Notations and preliminaries
2.1 Accelerated rate for Bellman consistency operator
2.2 Accelerated rate for Bellman optimality opera
5 Approximate Anchored Value Iteration
6 Gauss–Seidel Anchored Value Iteration
7 Conclusion, Acknowledgments and Disclosure of Funding and References
E Omitted proofs in Section 5
First, we prove following key lemma.
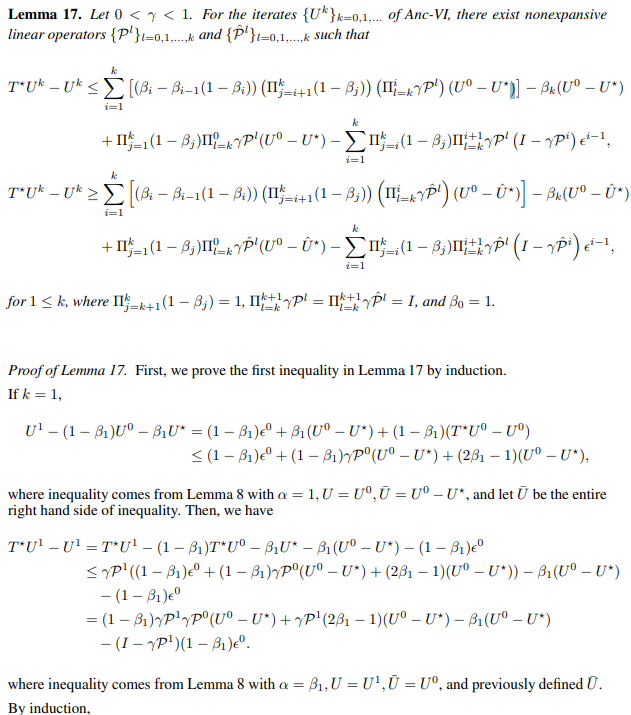
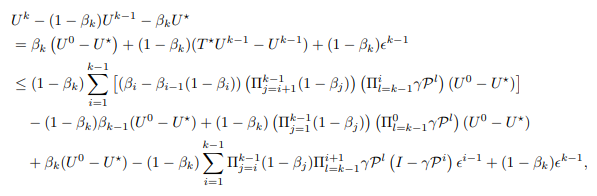
and let U¯ be the entire right hand side of inequality. Then, we have
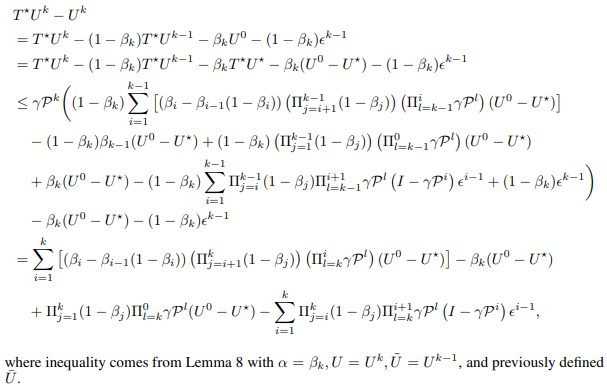
Now, we prove second inequality in Lemma 17 by induction.
If k= 1,
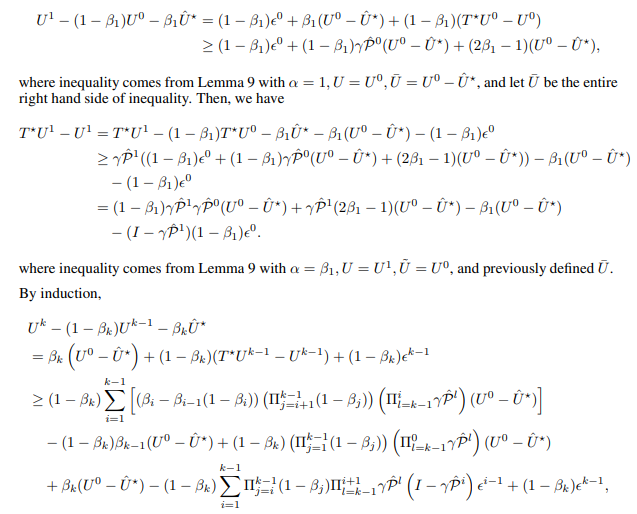
and let U¯ be the entire right hand side of inequality. Then, we have
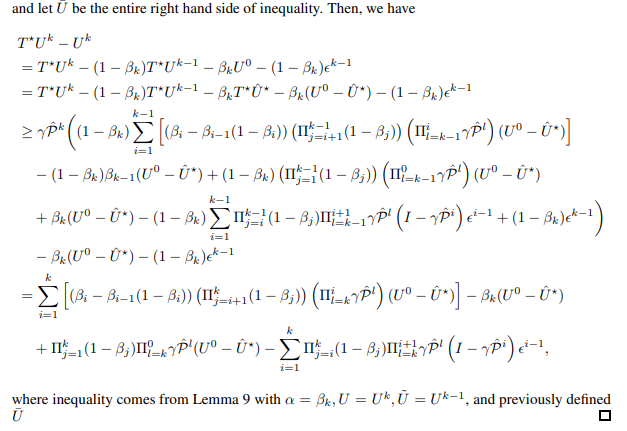
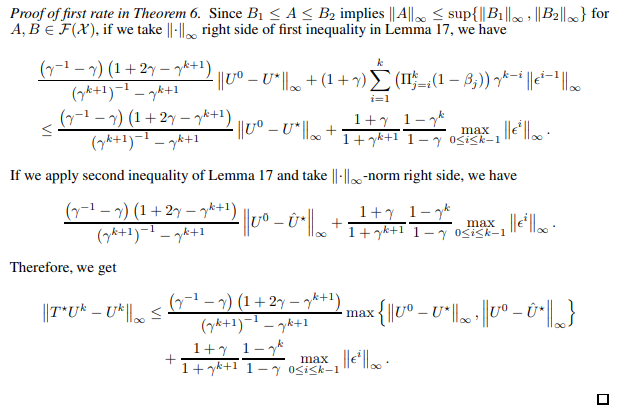
Now, we prove the first rate in Theorem 6.
Now, for the second rate in Theorem 6, we present following key lemma.



let U¯ be the entire right hand side of inequality. Then, we have
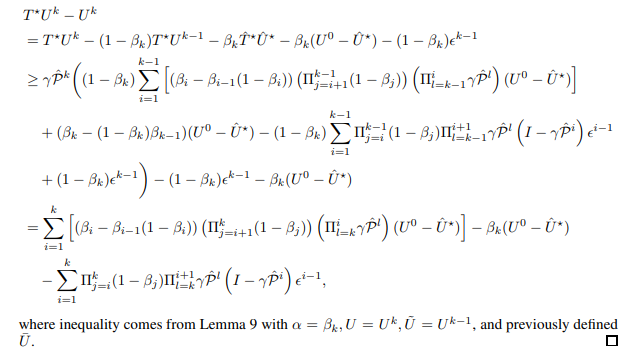
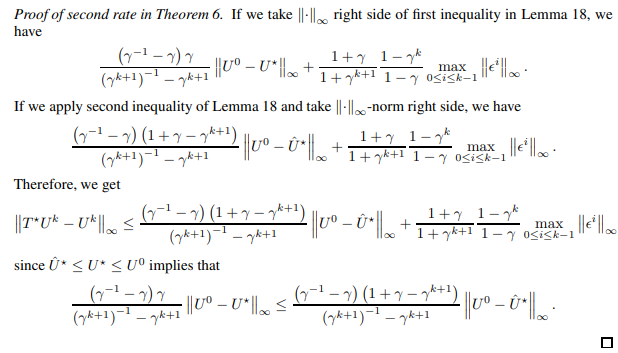
Now, we prove the second rate in Theorem 6.
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.